Dental Pulp and Root Canal Anatomy
INTRODUCTION
For the success of endodontic therapy, it is essential to have knowledge of general morphology, anatomy of dental pulp and root canal and its variations.
PULP SPACE
The pulp space is the central cavity within a tooth and is enclosed by dentin except apical foramen. This pulp space is divided into 2 parts.
- It occupies the coronal portion of the pulp. Pulp chamber acquires the shape according to external form of crown of teeth.
- Roof consists of dentin occulsally or incisally.
- Floor of pulp chamber merges into root canal at orifice.
PULP HORNS
It is an accentuation of roof of the pulp chamber directly under a cusp or developmental lobe.
CANAL ORIFICE
Canal orifices are the opening in the floor of pulp chamber to root canals.
ROOT CANALS
- Extends from canal orifices to apical foramen.
- Root canal is divided into three sections- Coronal, Middle and Apical thirds.
- In anterior teeth there is no distinction between pulp chamber and root canal but in multi-rooted teeth there is obvious distinction between pulp chamber and root canal i.e canal orifices.
APICAL ROOT ANATOMY
Following are seen in apical third of the root.
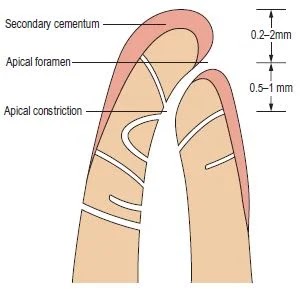
Apical Constriction (Minor Diameter)
- The Narrowest diameter of canal.
- Apical constrictions are found 0.5-1.0 mm away from the root apex.
Apical Foramen (Major Diameter)
- Main apical opening at or near the apex of root through which the blood vessels and nerves of the pulp enter or leave the pulp cavity.
- Its diameter almost double the apical constriction, which as been described as morning glory or hyperbolic.
- Apical foramen may not always be located at the center of apex.
Average Distance between major and minor diameter is 0.5 mm in young person and 0.67 mm in older person.
Cementodentinal Junction (CDJ)
- CDJ is a point in a canal where cementum meets dentin.
- Position of CDJ usually lies 0.5-1 mm from the apical foramen.
Apical Delta
it is a trangular area of the root surrounded by main canal, accessory canal and peri-radicular tissue.
SIGNIFICANCE OF APICAL THIRD
- Apical constriction acts as natural stop for obturation.
- Treatment of apical part is very difficult due to presence of accessory and lateral canals.
- Most of the curvature occurs in apical third.
- Size and shape of apical foramen should always be maintained.
- During endodontic surgery, 3mm of apical root is resected because of apical abberations.